Simulation is not the only type of Modeling
Various types of models are used to solve business problems
Mental Models

Diagrams
Physical Models

Formulas

Tables
What is simulation for
Supply chain design & optimization

Business processes optimization

Inventory management

Facilities optimization

Integrated planning

Risk Management
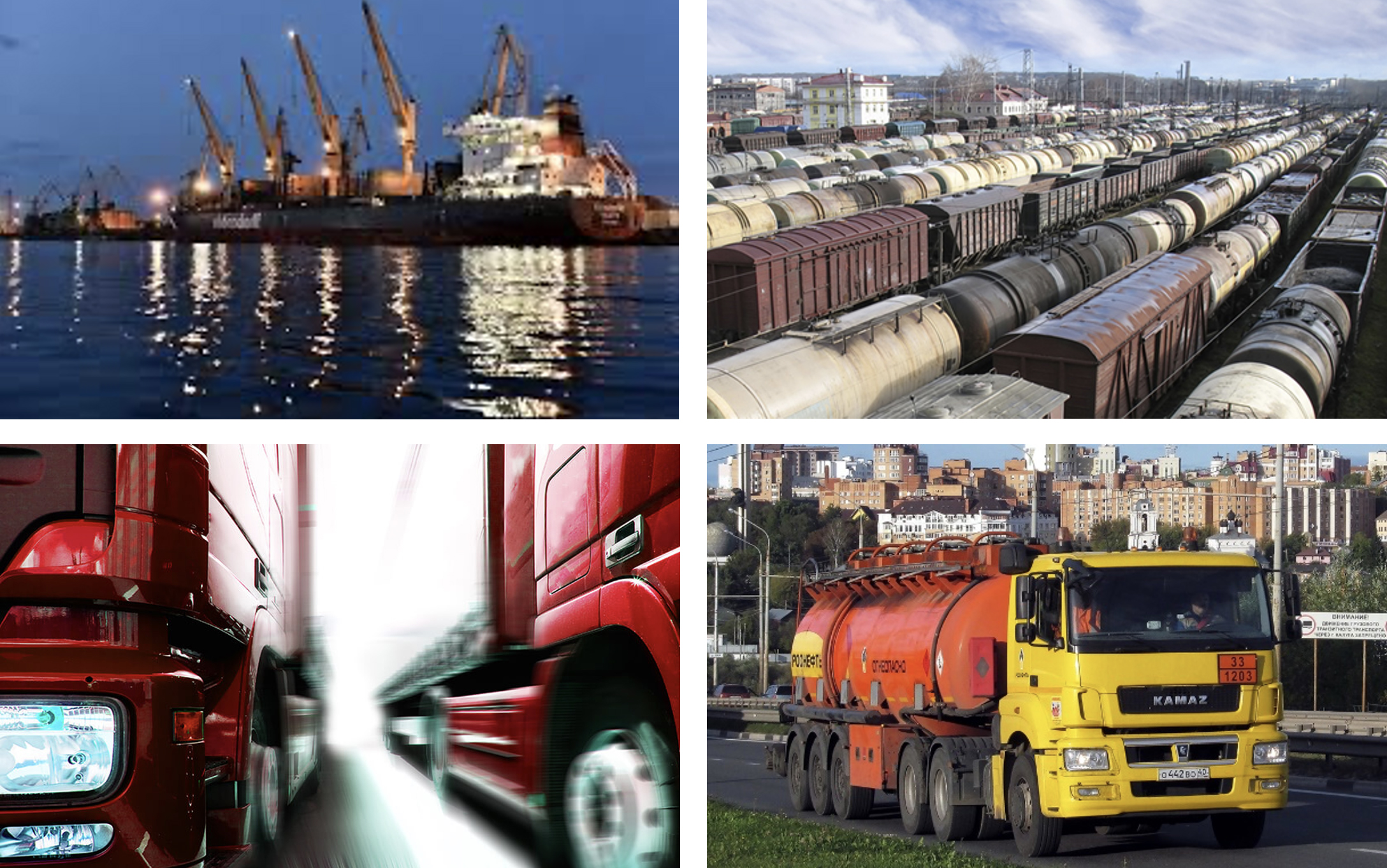

The success of any business depends on many related parameters. Only part of business factors and situations is predictable, the other is probabilistic. Simulation models takes into account many such complex factors that determine the result of business. Simulation modeling is a tool for solving a wide range of tasks
Models of manufacturing and Logistics
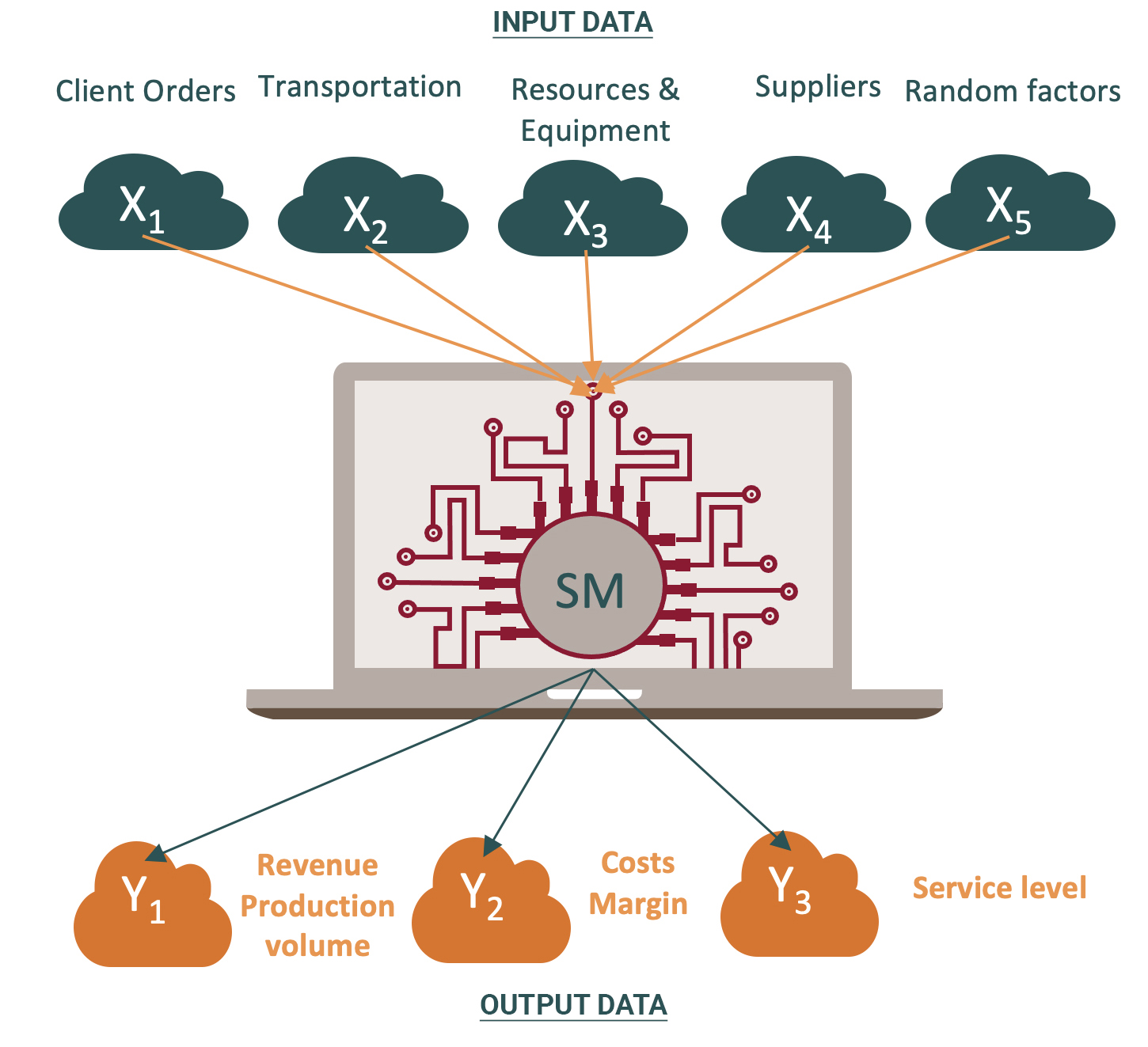
The simulation model is a program that simulates the operation of an object based on specified input data, rules and logic of operation, laws of distribution of random factors and variable parameters. The model generates a set of output data that gives a complete picture of the object’s operation

Optimization of the technological chain, production resources

Optimization of warehouse equipment, and personnel

Cargo flow planning across the entire supply chain

Assessment of the impact of force majeure situations on business

Determining optimal business processes and inventory management policies

Production personnel planning

Equipment workflow optimization

To build a simulation model specifically for your company, the analysis of statistics for past periods and business plans is used
The model can be integrated with your accounting system

The model obtains the state of the system at the output on the base of inputs, operating rules, and random factors

The model allows you to compare the specified process implementation options and search for optimal parameter values
Anylogic
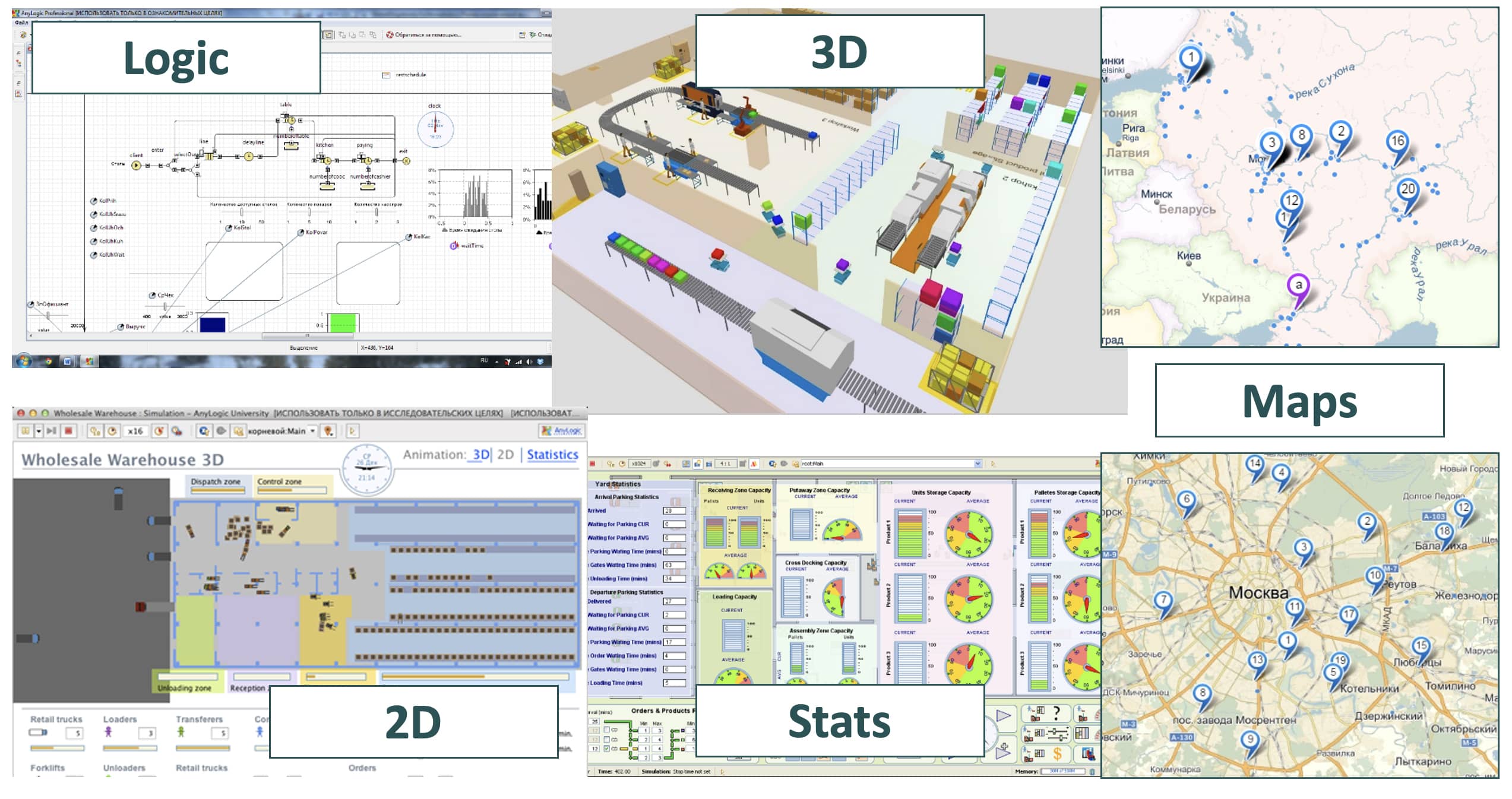
Basic Elements of a Model
- Logic – created from model objects (blocks and agents)
- User interface (2D and 3D)
- Changing the scale of time
- Geographical maps (if necessary)
- Tools to collect and analyze statistics
- Tools for integration into corporate IT
Input data
- Equipment
- Speed
- Staff… etc.
Scenarios
- Hypotheses “To Be”
- Demand
- New products and customers… etc.
Force majeure factors
- Weather
- Accidents/Mistakes/Diseases … etc.